Can artificial intelligence (AI) be used to identify anatomy within the surgical field? This was a question explored by surgical experts including Adnan Alseidi, MD, MEd, UCSF Department of Surgery faculty and UCSF Center for Intelligent Imaging (ci2) member. In a multicenter study, a team of investigators sought to develop and evaluate the performance of AI models that can identify safe and dangerous zones of dissection, and anatomical landmarks during laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC), a surgical treatment of gallbladder disease.
"Many adverse events during surgery occur due to errors in visual perception and judgment leading to misinterpretation of anatomy. Deep learning and computer vision, a subfield of AI, can potentially be used to provide real-time guidance intraoperatively," said the team of investigators.
They developed and trained deep learning models to identify safe (Go) and dangerous (No-Go) zones of dissection, liver, gallbladder, and hepatocystic triangle during surgery. Expert surgeons performed annotations and then evaluated AI predictions against these annotations using 10-fold cross-validation. Primary outcomes were intersection-over-union (IOU) and F1 score (validated spatial correlation indices), and secondary outcomes were pixel-wise accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, standard deviation.
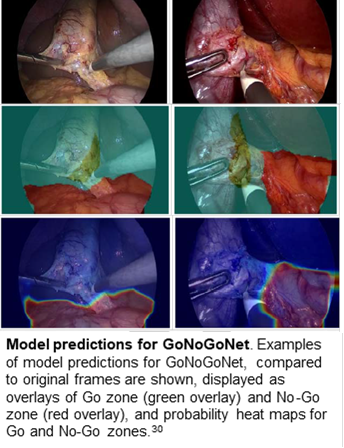
The team presented their findings this fall at Clinical Day (CLINICCAI), an event hosted by the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Society dedicated to clinical translation of medical image computing and computer assisted interventions. Their paper was published in the Annals of Surgery.
"Our study found that deep learning can be used to identify safe and dangerous zones of dissection and other anatomical structures during LC surgery," says Dr. Alseidi. "There is definitely more potential for surgical AI and surgical data science in the operating room (as a guide and/or as a coach), especially as we see more evidence on its safety and effectiveness in the operating room. This potential comes in the form of augment performance, real-time decision-support and other quality-improvement (QI) initiatives."