Principal author
Contributors
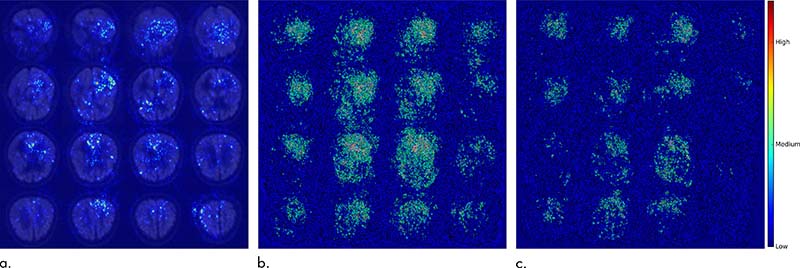
Combined deep learning techniques with brain imaging to discover changes in brain metabolism predictive of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Previous research had demonstrated a link between patterns of glucose uptake in the brain and the disease process, but biomarker discovery was lacking. Collaborating with Benjamin Franc, MD, Dr. Sohn trained a DL algorithm using more than 2,100 18-F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET scans from 1,002 patients – a dataset originating from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. After testing on an independent set of 40 scans from 40 patients never studied, the algorithm was able to predict every case that advanced to AD. Dr. Sohn’s next steps could include a larger multi-institutional prospective study using the algorithm, as well as training the tool further to spot patterns associated with the accumulation of beta-amyloid and tau proteins – a known AD biomarker.
Get involved
Are you researcher, doctor, or industry partner with something to contribute to this work? We want to hear from you. We welcome opportunities for collaboration and discussion.
